PG190442
Kartik Nakkana

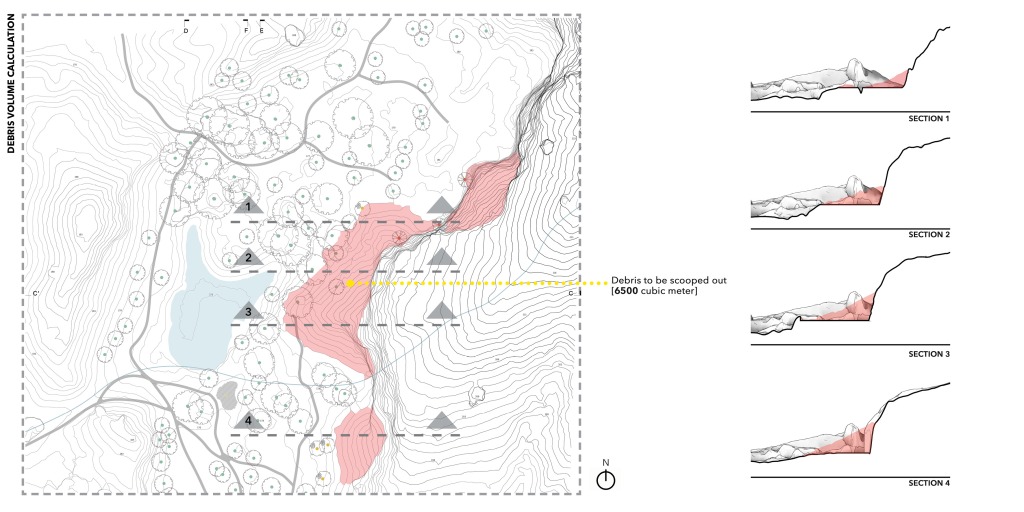
The map below shows 3 specific areas of eroded debris and rubble with the highest amount of porous soil. The project proposes to scoop out all the eroded material amounting up to roughly 6500 cubic meters of debris. The sections above shows the vacancies created by clearing out the eroded soil which provides an opportunity to appropriate a prosthetic in the newly formed vacancy.

The proposal is to create a mycelium ferrocement vault in the vacancy such that the eroded material falling on the top of the vault would be consolidated by means of biological colonization through mutation of mycelium in due course of time. The vault works as an ecotone because it not only acts a catalyst to biological colonization but also acts as a prosthetic between the inorganic architectural intervention and organic life form growth caused by the mycelium.




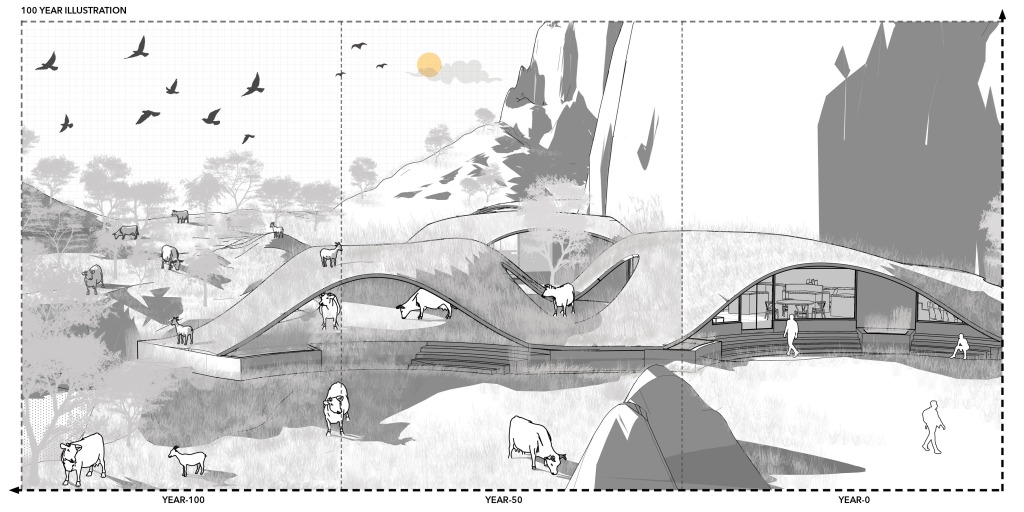
Center for permaculture aims to collaborate with the local herders and pastoralists in permaculture and regenerative grazing. The mycelium vault housing the program acts as a hybrid inorganic prosthetic to the site working as a catalyst to the processes. The training of the herds would eventually lead cattle to follow a cycle of grazing with occasional supervision. As the Centre takes care of the feeding and health supervision, the herders can explore new techniques of approaching pastoralism and permaculture. The animal droppings and plant waste is composted and turned into manure for the next cycle, with animal intervention clearing out weeds and balancing the biodiversity. The slow growth of vegetation also informs a slow increase in groundwater because of the roots’ water holding capacity, which eventually causes more vegetation. An increase in vegetation leads to more biodiversity as other species’ density like birds and other semi-feral creatures also increases. Recycling the waste keeps the energy cycle going, aligning with the crop cycle that repeats each season.

Each crop cycle with human intervention requires ten years to effectively recharge the water table of a given area. Within three such cycles (30 years), the ecosystem starts to mimic the cycles and requires less human intervention over time. Eventually, as the locals familiarize themselves with the permaculture practices, they can be the sole operators of the Centre’s activities without any additional support. The external human intervention decreases over time; the internal partitions can also detach from the building leaving only the mycelium roof. Over these years, the roof, which has already become an integral part of the site, now stands alone without permaculture activities and wildlife will eventually take over the space which once housed the program. This inorganic prosthetic would be left with the site while the program, which acted as a catalyst to the whole process, slowly removes itself from the site.






The illustration above explains the development of site plan using the natural water channels of surface runoff as trenches to identify possible spaces for artificial reservoirs. Vacancies created by overlapping these trenches with human and animal pathways are used for situating the built form. Permaculture center places itself near the water body overlooking the site, while animal sheds are placed at the vicinity of water bodies and grazing pockets

Illustration above shows open trenches and site drains used for surface runoff which are also part of sites water strategy. The location of surface runoff and trees affect the shape of the vault. Location of trees are also spaces applying the crescent berm water strategy

The corner most vaults are the livestock resting spaces with composting and fodder storage at the back with grazing pockets and water in their nearest vicinity. Workshop area are for collaborations between permaculture people and the local farmers overlooking the site. Workshop even opens up into administration and research labs. The seating of the administration is very non hierarchical and placed such that all occupants have maximum experience of the mountain coming into the office space. The research lab again overlooks the site with storage and toilets placed at the corners. All the vaults open into the central open to sky courtyard.

The illustration above is a section showing administration where the corners without enough head height uses planters or takes approach of taking the level down to place functions like meeting spaces. The dotted line represents the scooped out debris to place the vault



The illustration above show site section with the slope of the site directed towards the natural water body. All the excess from the artificial ponds is directed towards the natural pond
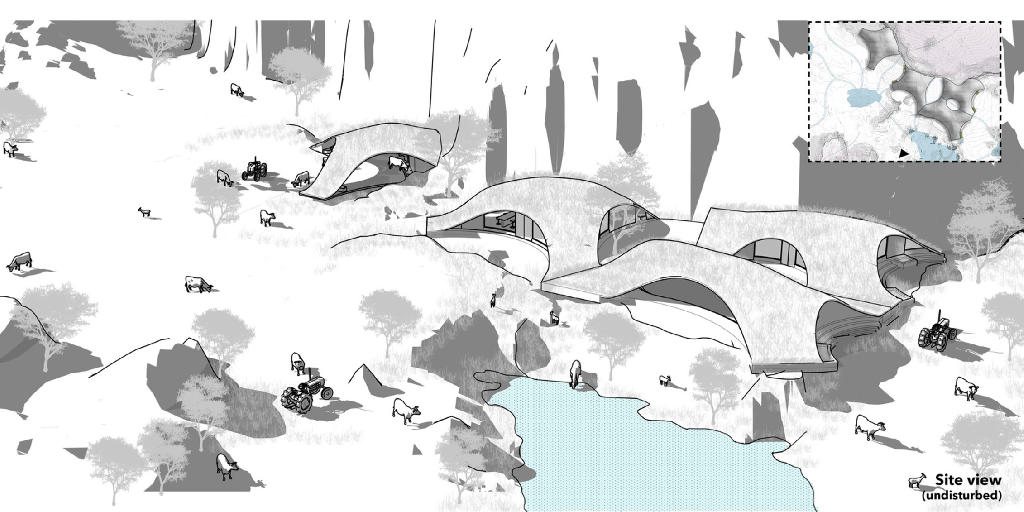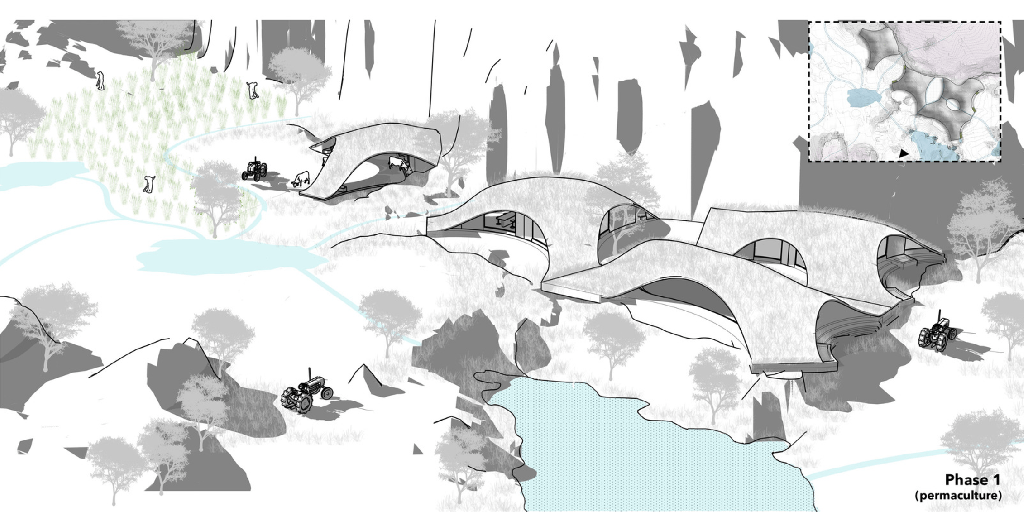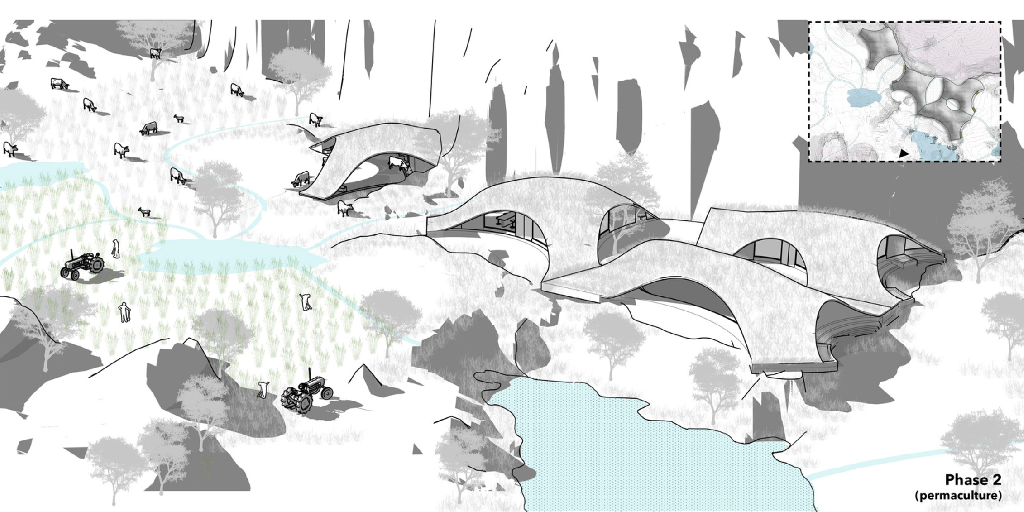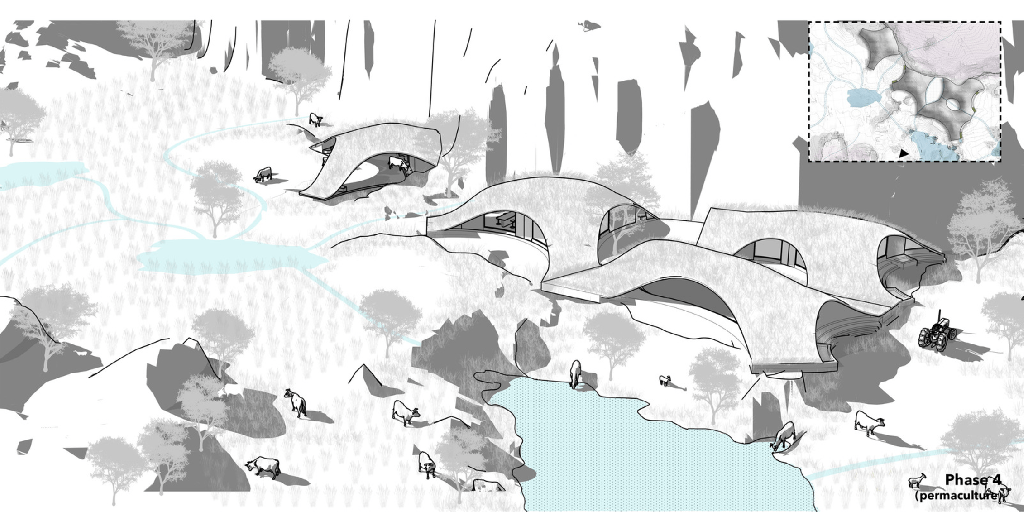
The illustration above explains permaculture approach of regenerative grazing. Excessive grazing can always lead to deforestation and hence phase wise development of site and grazing pattern helps develop agromemory for the users both humans and animals alike in way to keep the water table at check. The water channels automatically create vacancies which serve as grazing pockets for systematic grazing and afforestation of the site. In phase 4 the permaculture practice jumps to the other side of the site repeating the same cycle, slowly rejuvenating the sites water table while the cattle doesn’t overgraze controlling both weed growth and wilding process



